QTrobot: Your Online AI Data Assistant
Source code: Check the source code here
The Online AI Data Assistant is a flexible, cloud-enhanced version of the QT AI Assistant, designed for QTrobot models that do not include dedicated GPU hardware, such as QTrobot-i5 and QTrobot-i7. Built upon the powerful LlamaIndex framework, this demo enables QTrobot to serve as a conversational AI assistant that can ingest, index, and intelligently respond to user queries over custom documents and online content.
Table of Contents
- Features
- Technologies Used
- Getting Started
- Installation
- Usage
- Customization
- Choosing a different LLM model ftom Groq Cloud
- Choosing models (GPT4-o) ftom OpenAI
- Using Azure Speech recognition
- Using Google Speech recognition
- Using a different converation language
- Using different document formats
- Customizing the QTrobot's Role
- Disabling Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- Storing and restoring conversations
- Command-line parameters
- QTrobot Online Data Assistant - Web UI Access
- License
Features
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Enhances QTrobot's ability to provide accurate and context-aware answers by retrieving relevant information from user-provided documents (e.g.
.txt,.pdf,.docx,.md) and simple web pages. This retrieval is powered by semantic search over documents indexed locally using Faiss or in the cloud using AstraDB. -
Multilingual Query Support: Supports queries in a wide range of languages, regardless of the language used in the original data source. Users can freely interact with their content in the language they are most comfortable with.
-
Online Large Language Models (LLMs): Integrates with a variety of cloud-based LLMs (e.g. OpenAI, Groq) to generate fluent, context-aware responses. The modular design allows easy expansion to new LLM providers via LlamaIndex.
-
Online Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Offers real-time speech-to-text using multiple online services—including Groq (Whisper), Azure Speech Service, and Google Speech Service. Users can select the ASR provider that best matches their needs for performance, cost, or regional support.
-
Web Data Ingestion: In addition to local documents, this version can scrape and index web pages, allowing dynamic expansion of its knowledge base without manual upload steps.
-
Flexible, Cloud-Based Architecture: This assistant is optimized for QTrobots without dedicated GPU hardware. Its modular design also makes it ideal for evolving deployments and diverse connectivity scenarios.
-
Provider Choice & Cost Optimization: Gives users control over which ASR, LLM, or vector store service they use—enabling smarter, cost-effective customization of their AI assistant setup.
Technologies Used
Following is an overview of the key technologies and services employed to implement each feature of the QTrobot: Your Online AI Data Assistant. These tools were selected for their flexibility, extensibility, and ability to operate efficiently in resource-constrained, GPU-less environments while offering robust cloud integration.
-
Online Large Language Models (LLMs): Integration with cloud-based models such as GPT-4, GPT-4o, and GPT-4o-mini from OpenAI, as well as LLaMA 3, LLaMA 3.1, LLaMA 4, and Google Gemma2 via Groq API. These models provide high-quality, multilingual, and context-aware natural language responses. Integration is handled through LlamaIndex, ensuring abstraction and extensibility across LLM providers.
-
Online Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Supports real-time transcription using multiple online ASR services including Groq Whisper, Azure Speech Service, and Google Speech Service. These services collectively support over hundreds of languages and dialects, enabling versatile, multilingual voice interaction.
-
Offline Voice Activity Detection (VAD): Utilizes Silero VAD, a highly accurate and lightweight offline voice activity detector, to identify when a user is actively speaking. This allows the system to initiate ASR streaming only during detected speech, significantly reducing unnecessary API usage, network traffic, and associated costs.
-
Vector Store (RAG Backend): Faiss or AstraDB is used for storing document embeddings and enabling fast semantic search locally or in the cloud.
Faiss (Facebook AI Similarity Search) is a highly optimized library developed by Meta for efficient similarity search and clustering of dense vectors. It is ideal for local deployments, offering fast in-memory indexing and search with various indexing strategies to balance speed and memory usage.
AstraDB, on the other hand, is a cloud-native, serverless vector database built on Apache Cassandra. It is designed for scalability and elasticity in distributed environments, making it suitable for remote or hybrid deployments that require persistent storage, cross-device access, or integration with other cloud services.
Thanks to LlamaIndex's vector store abstraction, the implementation can be easily adapted to a variety of alternative vector databases such as Pinecone, Qdrant, or Chroma, allowing developers to choose the most appropriate backend based on performance, storage requirements, or infrastructure preferences.
-
Data Ingestion & Web Integration: Document ingestion and chunking are powered by LlamaIndex, supporting formats such as
.pdf,.txt,.docx, and.md. Additionally, it includes a web connector layer that allows scraping and indexing of simple HTML pages. This can be extended via tools like SpiderWeb and other LlamaIndex web connectors to handle richer web content extraction. -
Text-to-Speech (TTS): The assistant uses the default Acapela TTS engine provided by QTrobot for speech synthesis. This engine supports multiple voices and languages and ensures real-time verbal responses fully offline.
-
Runtime & Deployment: All services and processing run natively on QTrobot-i5 and QTrobot-i7 platforms without requiring GPU support. The architecture is fully self-contained and optimized for embedded execution, ensuring that the robot remains responsive and operational without dependency on external compute infrastructure.
Getting Started
The QTrobot Online Data Assistant can run on all variants of QTrobot for Research version.
Installation
- The project's source code is available in the LuxAI Tutorials Github Repository. To get the latest version of the code on your QTPC:
cd ~/robot/code/tutorials/; git pull - Ensure that software repository on QTPC is updated and service files for
qt_respeaker_appis installed in your catkin workspace:cd ~/robot/code/software/; git pullcd ~/catkin_ws/; ln -s ~/robot/code/software/headers/qt_respeaker_app/ ./srccd ~/catkin_ws/; catkin_make
- Throughout this documentation, we will refer to "~/robot/code/tutorials/demos/qt_ai_data_assistant_online" as "qt_ai_data_assistant_online".
The default installation is configured to use Groq Cloud for both LLM and ASR services. If you prefer to use models from OpenAI or Azure and Google ASR instead, please refer to the instructions in the the Customization section.
-
Setup Groq clould API key:
- Visit Groq cloud console to create a FREE API Key.
- Configure your API key as an environment variable. To do that edit
~/.bash_aliasesfile and add the following line:export GROQ_API_KEY="<you-api-key>"
-
Install required python packages:
- Create a python3 virtual environment and install pip packages:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Create a python3 virtual environment and install pip packages:
Usage
Run the QTrobot Online Data Assistant with demo data:
The repository includes a demo PDF file detailing the QTrobot research variants and specifications. To run the project with this demo document:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py
Wait a few seconds for the script to initialize and load the document. Once it's ready, you can begin conversing with the QTrobot. For example, you might ask, "What are all your variants?" or "How can I program QTrobot?" You can also ask questions unrelated to the document, such as, "What are the official languages of Luxembourg?"
Run the QTrobot Online Data Assistant with your own data:
To run the QTrobot Online Data Assistant with your own data, first create a folder to store your documents:
mkdir ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data
Copy your PDF file(s) into your project's document folder (~/Documents/qt-assistant-data). For example, you can use one of your research papers. Then, simply start the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script and provide the path to your document folder.
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --docs ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data --reload
Wait a few seconds for the script to initialize and reload (--reload) the document. Once it's ready, you can ask questions about the content of your PDF.
Run the QTrobot Online Data Assistant with data from Web:
QTrobot Online Data Assistant can scrape and index dimple HTML web pages, for example news pages.
To run the assitant with online data, simply provide the urls as follows:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --source web --urls https://lite.cnn.com/ --reload
When it started and fetch the new page, you can ask questions about the latest news.
Customization
You can customize the demo project in various ways to suit your needs:
Choosing a different LLM model ftom Groq Cloud:
By default, QTrobot Online Data Assistant uses the Google Gemma2 llm for conversation. However, you can experiment with different LLMs, such as Mata Llama 3.1 to explore varying conversational styles, performance, or domain-specific knowledge. To use a different model start the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script and specify the LLM model as a parameter:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --llm-engine groq --llm-model llama-3.1-8b-instant
You can see all Groq cloud supported models here.
Choosing models (GPT4-o) ftom OpenAI:
By default, QTrobot Online Data Assistant uses models from Groq cloud. However, you can use more advanced models from OpenAI such as GPT4 and GPT4-o. To do that:
- Login OpenAI Developer platform and create new secret key.
- Configure your API key as an environment variable. To do that edit
~/.bash_aliasesfile and add the following line:export OPENAI_API_KEY=="<you-openai-api-key>"
next start the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script and specify the LLM engine and model as parameters
source ~/.bash_aliases
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --llm-engine openai --llm-model gpt-4o-mini
You can see all OpenAI supported models here.
Using Azure Speech recognition:
Azure Speech Service offers highly accurate, enterprise-grade automatic speech recognition with extensive language support (100+ languages and variants) and regional availability, making it a strong choice for international deployments. For developers interested in trying it out, Azure offers a Free Tier ideal for development and testing.
To get started, you'll need an AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY and AZURE_REGION. Follow the official Microsoft guide here Create an Azure Speech resource and get your subscription keys
Next configure your subscription keys as an environment variable. To do that edit ~/.bash_aliases file and add the following line:
export AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY="<your-azure-subscription-key>"
export AZURE_REGION="<your-azure-service-region>"
Ensure azure-cognitiveservices-speech python package is installed in your project's virtual environemnt:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
pip install azure-cognitiveservices-speech
Start the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script and specify the Azure ASR engine as parameter:
source ~/.bash_aliases
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --asr-engine azure
Using Google Speech recognition:
Google Cloud Speech-to-Text provides real-time, high-accuracy transcription powered by Google's deep learning models. It supports 125+ languages and variants, making it a solid choice for multilingual and global deployments.
To get started, follow the setup guide from Google: Transcribe audio using client libraries. You will need to export your Google Cloud credentials in a .json format and save them to your QTrobot (QTPC). Once you've downloaded your credentials:
Edit your ~/.bash_aliases file and add the following line:
export GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS="/home/qtrobot/google_speech_key.json"
Make sure the google-cloud-speech Python package is installed in your virtual environment:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
pip install google-cloud-speech
Then start the assistant and specify the Google ASR engine:
source ~/.bash_aliases
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --asr-engine google
Using a different converation language:
QTrobot Online Data Assistant supports multilingual interaction, allowing users to query and receive responses in a language different from that of the original document. Language support depends on the multilingual capabilities of the selected LLM and ASR service. Most LLMs mentioned in this tutorial—such as Gemma2, LLaMA 3.1, and various OpenAI models—offer robust support for multiple languages. However, to ensure a seamless conversational experience, you must also verify that the selected language is supported by QTrobot's Text-to-Speech (TTS) system.
To launch the demo in a specific language (e.g. French), run the following command:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --lang fr-FR
The --lang <lang code> parameter automatically sets both the ASR input language and the TTS output language for the conversation.
You can also change the conversation language dynamically through the built-in Web UI. To do so, open a browser on the QTPC and visit: 127.0.0.1:6060.
Note: If the desired TTS language is not installed on your QTrobot, please contact support@luxai.com to obtain the necessary language files.
Using different document formats:
By default QTrobot Online Data Assistant loads PDF (.pdf) documents from the specified directory. It uses the LlamaIndex Data Framework to support various document formats such as .txt, .docx and .md. You can specify the document formats and the maximum number of files to load using the appropriate parameters.
For example, to load a maximum of 5 PDF and DOCX files from ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data, use the following commands:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --formats .pdf .docx --max-docs 5
Customizing the QTrobot's Role
You can customize the role and behavior of QTrobot by modifying the system role in the LLM prompts. This allows you to adapt QTrobot to different scenarios, making it a versatile assistant tailored to specific tasks or environments. By changing the system role, you can guide how QTrobot responds, behaves, and interacts with users.
Why Customizing the Role is Interesting
Customizing the system role allows you to adapt QTrobot to a wide range of applications beyond its default educational and research-focused roles. Whether you need QTrobot to act as a receptionist, a healthcare assistant, a tourist guide, or any other role, this flexibility makes QTrobot a powerful tool in various environments. By fine-tuning the system role, you can ensure that QTrobot meets the specific needs of your users, providing a more personalized and effective experience. Additionally, by leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), QTrobot can provide highly relevant and contextual responses based on user-provided documents and data, enhancing its utility in specialized roles.
The default system role is defined in the config/default.yaml file:
- name: "role"
type: "str"
label: "Robot role"
description: "This is the LLM system prompt which define the robot's role"
ui:
element: "textarea"
scope: "runtime"
default: |
You are a humanoid social robot assistant named "QTrobot". You can hear and talk. You are designed to support various use cases, including the education of children with autism and other special needs, as well as human-robot interaction research and teaching.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
To modify QTrobot’s role, you can edit the relevant part of system_role section in the llm_prompts.py file. By changing the system role, you can assign QTrobot a new identity and set of behaviors. Here are some examples of how you might customize QTrobot's role, emphasizing its ability to use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide insightful responses based on user-provided data:
-
Example 1: Receptionist
Transform QTrobot into a virtual receptionist who can greet visitors, provide information, and answer queries based on company documents or FAQs:
- name: "role"
type: "str"
label: "Robot role"
description: "This is the LLM system prompt which define the robot's role"
ui:
element: "textarea"
scope: "runtime"
default: |
You are a receptionist named "QTrobot". Your job is to greet visitors, answer their questions, and provide information based on the company’s documents.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
... -
Example 2: Tourist Guide
QTrobot can act as a virtual tourist guide, offering information about local attractions, history, and travel tips by pulling data from guidebooks, maps, and other resources
- name: "role"
type: "str"
label: "Robot role"
description: "This is the LLM system prompt which define the robot's role"
ui:
element: "textarea"
scope: "runtime"
default: |
You are a tourist guide named "QTrobot". Your role is to provide tourists with information about local attractions, history, and travel tips based on guidebooks and other documents.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
... -
Example 3: Research Conference Center Assistant
Transform QTrobot into a virtual conference assistant that helps attendees navigate the event, find sessions, and get information about workshops and presentations:
- name: "role"
type: "str"
label: "Robot role"
description: "This is the LLM system prompt which define the robot's role"
ui:
element: "textarea"
scope: "runtime"
default: |
You are a conference assistant named "QTrobot" at a research conference center. Your role is to assist attendees by providing information about the venue, schedule, workshops, and research presentation sessions.
Provide clear and concise information about the conference schedule, including session times and locations only from the provided documents.
Use a polite and professional tone.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
Disabling Retrieval-Augmented Generation:
In some cases, you may not need to use the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) feature, especially if the application does not require any user-provided documents or knowledge. Disabling RAG allows QTrobot to interact directly with the LLM for faster, more fluent conversations, as it reduces the processing overhead and latency associated with retrieving and integrating external data.
To disable RAG, simply start the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script with the --disable-rag parameter:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant_online
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --disable-rag
When RAG is disabled, QTrobot will no longer retrieve information from documents or external sources, and all responses will be generated directly by the LLM based on the content provided in the system_role. This can improve response times and is ideal when external knowledge retrieval is not needed for your use case.
Storing and restoring conversations
To save the entire conversation and restore it later, simply run the qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py script and specify the path to the JSON file where the conversation memory will be stored.
- If the JSON file already exists, the conversation memory will be loaded from it at the start.
- If the file does not exist, a new one will be created to store the conversation.
Example usage:
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --mem-store ~/chat_store.json
Command-line parameters
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py --help
usage: qt_ai_data_assistant_online.py [-h] [--source SOURCE] [--urls URLS [URLS ...]] [--docs DOCS] [--formats FORMATS [FORMATS ...]] [--max-docs MAX_DOCS] [--reload] [--llm-engine LLM_ENGINE] [--llm-model LLM_MODEL]
[--asr-engine ASR_ENGINE] [--mem-store MEM_STORE] [--paused] [--lang LANG] [--disable-rag] [--volume VOLUME]
Configuration for the QT AI Agent application
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--source SOURCE Asr engine to use. Default is groq.
--urls URLS [URLS ...]
list of urls to load data from using simple web reader.
--docs DOCS Path to the folder containing documents to load.
--formats FORMATS [FORMATS ...]
Document formats ('.txt', '.pdf', '.docx', '.md').
--max-docs MAX_DOCS Maximum number of document files to load.
--reload Reload data from web or local. Default is false.
--llm-engine LLM_ENGINE
LLM Server engine to use. Default is groq.
--llm-model LLM_MODEL
LLM model to use. default is gemma2-9b-it.
--asr-engine ASR_ENGINE
Asr engine to use. Default is groq.
--mem-store MEM_STORE
Path to a JSON file (e.g., ./chat_store.json) to store and restore the conversation memory.
--paused Pause and Resume the interaction
--lang LANG Conversation language (ar-AR, en-US, en-GB, de-DE, es-ES, es-US, fr-FR, hi-IN, it-IT, ja-JP, ru-RU, ko-KR, pt-BR, zh-CN).
--disable-rag Disable Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
--volume VOLUME Robot's speaker volume level.
QTrobot Online Data Assistant - Web UI Access
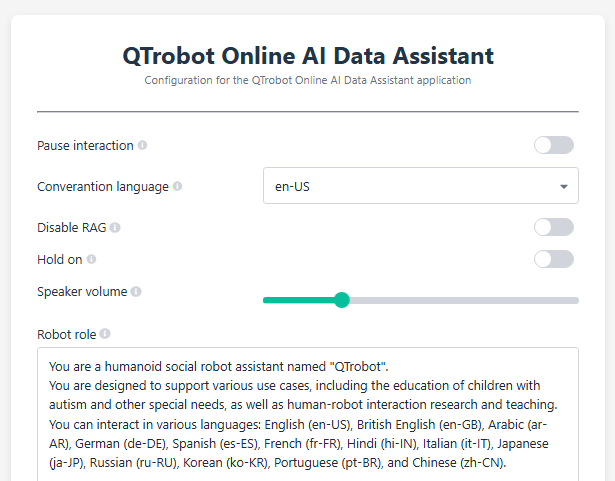
The QTrobot Online Data Assistant utilizes the Paramify module to provide a web-based interface for modifying runtime parameters.
Through this interface, you can easily change of the paramaters such as setting language, or pausing and resuming the conversation, among other adjustments.
To access the Web UI:
- Open a web browser on the QTPC.
- Navigate to http://127.0.0.1:6060.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Copyright
© 2024 LuxAI S.A. All rights reserved.