QTrobot: Your AI Data Assistant
Source code: Check the source code here
Requirements: QTrobot AI@Edge
The AI Data Assistant is a project that demonstrate how to transform QTrobot (QTrobotAI@Edge) into a powerful, on-device AI assistant capable of engaging in natural voice conversations. By integrating advanced technologies such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Offline LLM, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Scene Understanding via Visual Language Models (VLM), and Text-to-Speech (TTS), QTrobot can now understand, process, and provide insightful responses based on user-provided documents, visual inputs, and data in various spoken languages. To enhance the naturalness of interactions, QTrobot actively tracks the user's face and voice during conversations.
This project is designed to showcase QTrobot's ability to serve as a private, secure, and highly customizable data assistant. Users can simply upload their documents (e.g., PDFs, Microsoft Word) to QTrobot and start asking questions or requesting information, all through natural voice interaction. The entire process happens on-device, ensuring privacy and security for the user's data.
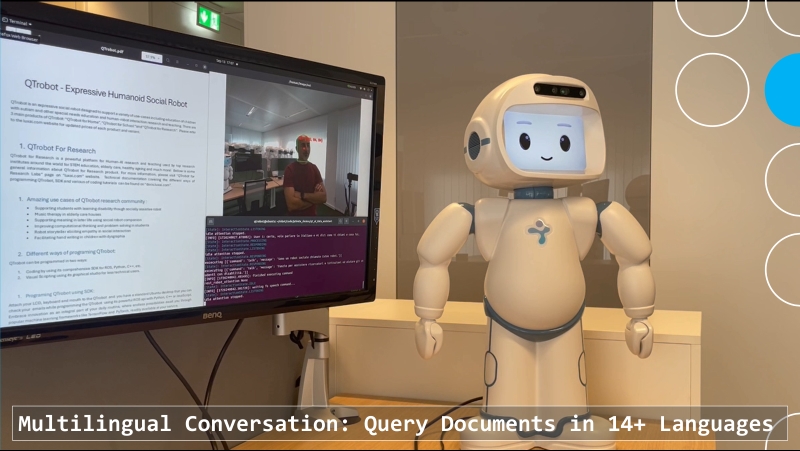 |  | 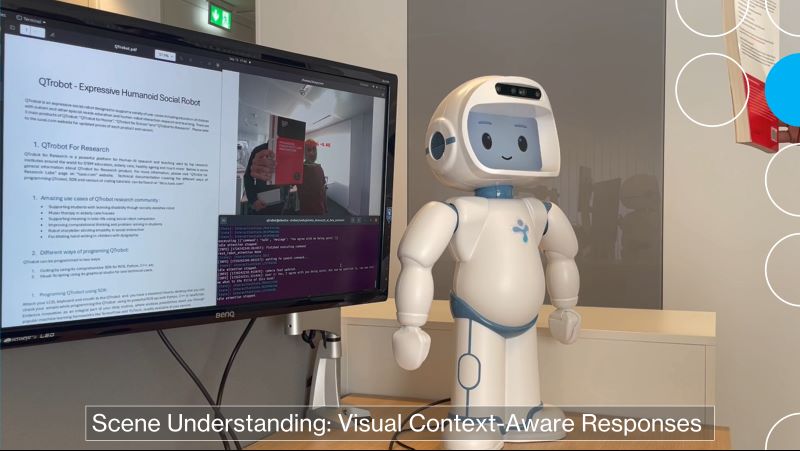 |
|---|---|---|
| Watch Multilingual Conversation Video | Watch Multi-User Conversation Video | Watch Scene Understanding Conversation Video |
Table of Contents
- QTrobot: Your AI Data Assistant
- Features
- Technologies Used
- Getting Started
- Installation
- Usage
- Customization
- License
Features
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Enhances QTrobot's ability to provide accurate and context-aware answers by retrieving relevant information from user-provided documents in various format such as '.txt' '.pdf', '.docx' and '.md'.
-
Multilingual Query Support: Allows users to query their data in a different language than the one used in the provided document. Indpended from the in which language the documents data are, users can ask questions regarding their data in more than 14 languages.
-
Offline Large Language Models (LLM): Enables QTrobot to generate human-like text and engage in meaningful conversations using state-of-the art llms such as Meta LLama3.1, Google gemma2, Microsoft Phi3 and Mistral.
-
Offline Scene Undertanding (VLM): Uses Visual Large Language Models (VLM) to interpret visual inputs from camera stream. QTrobot can analyze scenes, recognize objects, and infer context, enabling it to provide responses based on visual cues.
-
Multi-User Interaction: QTrobot recognizes and remembers users by their faces, personalizing interactions. It tracks individual preferences, recalls past conversations, and adapts to each user's needs for seamless engagement.
-
Human Tracking: Tracks the user's face and voice during interactions to make conversations feel more natural and engaging.
-
On-Device Processing: Ensures that all data processing occurs locally on QTrobot, protecting user privacy and maintaining security.
Technologies Used
Following is an overview of the key technologies and packages employed to implement each feature of the QTrobot Data Assistant. These tools were chosen to ensure robust performance, privacy, and seamless interaction in all user scenarios.
-
Offline Large Language Model (LLM): Llama 3.1 via Ollama Framework. Ollama is a framework designed to simplify the deployment and usage of large language models like Llama 3.1 in local environments. Ollama also supports advanced features like tool calling, enabling models to interact with external tools, APIs, and services, thus expanding their functionality beyond text generation. Llama 3.1 is a state-of-the-art open-source language model developed by Meta, renowned for its superior natural language processing capabilities. It supports multilingual applications, offers extended context handling of up to 128K tokens with very fast response time.
-
Offline Scene Undertanding (VLM): Moondream is a compact, highly efficient Vision-Language Model (VLM) designed to interpret visual data such as images and video streams. It is particularly adept at tasks like image captioning, object recognition, and answering questions about visual content, providing fast responses. This makes it ideal for applications such as robotics where real-time visual understanding is essential.
-
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Nvidia RIVA ASR. RIVA is an advanced offline automatic speech recognition engine optimized for high accuracy and low latency. It efficiently converts spoken language into text, making it ideal for real-time applications like interactive conversations. Riva supports multiple langueges such as English, Spanish, French, Italian and more. Check the supported languges here.
-
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): LlamaIndex Data Framework. LlamaIndex enables Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) by combining the strengths of data retrieval with text generation. This approach ensures that QTrobot can generate contextually relevant and accurate responses based on user-provided documents. The framework is scalable and flexible, handling large datasets efficiently and adapting to various formats of data inputs.
-
Multi-user Tracking and Interaction: DeepFace is a lightweight Python library that offers robust face recognition and analysis capabilities, used by QTrobot to track and maintain focus on the user's face during interactions. This enhances the naturalness and engagement of conversations by allowing QTrobot to respond accurately in real-time. it is a hybrid face recognition framework wrapping state-of-the-art models such as VGG-Face, FaceNet, OpenFace, DeepFace, DeepID, ArcFace, Dlib, SFace and more.
-
Text-to-Speech (TTS): QTrobot default TTS SDK using Acapela. The QTrobot TTS SDK converts text into natural, human-like speech. With support for a wide array of voices and languages, it enhances the interactivity and accessibility of QTrobot across different regions and languages.
-
On-Device Processing: QTrobotAI@Edge's Nvidia Jetson AGX Orin GPU. It provides the computational power necessary for QTrobot to perform intensive AI tasks directly on the device. This ensures high-performance processing and responsivness of AI models which is crucial for implementing fluent conversation. By processing all data on-device, it enhances data privacy and security, making it a key component of QTrobot's AI-driven operations.
Getting Started
The QTrobot Data Assistant requires QTrobotAI@Edge and an initial internet connection for installation and setup.
Installation
- The project's source code is available in the LuxAI Tutorials Github Repository. To get the latest version of the code on your QTPC (Nvidia Jetson):
cd ~/robot/code/tutorials/; git pull - Ensure that software repository on QTPC is updated and service files for
qt_respeaker_appis installed in your catkin workspace:cd ~/robot/code/software/; git pullcd ~/catkin_ws/; ln -s ~/robot/code/software/headers/qt_respeaker_app/ ./srccd ~/catkin_ws/; catkin_make
- Throughout this documentation, we will refer to "~/robot/code/tutorials/demos/qt_ai_data_assistant" as "qt_ai_data_assistant".
The installation process involves three main steps: (1) Installing Nvidia Riva ASR, (2) Installing Ollama and required models and (3) Installing python packages
-
Install Nvidia Riva ASR:
-
Sign in to your Nvidia NGC portal (sign up if you don't have an account).
-
Follow the instructions for Generating Your NGC API Key to obtain an API key.
-
Use your API key to log in to the NGC registry by entering the following command and following the prompts.
Note: The
ngcCLI is already installed on the QTrobot, so no need to install it.ngc config set -
Download the Embedded Riva start scripts to the
~/robotfolder using the following command:cd ~/robot/
ngc registry resource download-version nvidia/riva/riva_quickstart_arm64:2.14.0 -
Modify
~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0/config.shto disable unnecessary services, keeping onlyservice_enabled_asrenabled. The relevant part ofconfig.shshould look like this:# ...
# Enable or Disable Riva Services
service_enabled_asr=true
service_enabled_nlp=false
service_enabled_tts=false
service_enabled_nmt=false
# ... -
Update the
~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0/riva_init.shscript to resolve the Nvidia NGC CLI version issue by changing the version from3.26.0to3.63.0. Replace the URL on line 170 with:# Original line:
# https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/resources/nvidia/ngc-apps/ngc_cli/versions/3.26.0/files/ngccli_arm64.zip
# Updated line:
https://api.ngc.nvidia.com/v2/resources/nvidia/ngc-apps/ngc_cli/versions/3.63.0/files/ngccli_arm64.zip -
Initialize the Riva ASR container. This may take around 30 minutes, depending on your internet speed.
cd ~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0
bash ./riva_init.sh
-
-
Install ollama and pull the required models:
-
We have prepared a script (
install_ollama.sh) to download and install the appropriate version of ollama on QTrobot's Jetson AGX Orin. To install Ollama, execute the following command:cd qt_ai_data_assistant
sudo bash ./scripts/install_ollama.sh -
Next, download the required models. These models are approximately 6 GB in size, so the download may take some time. If the download process is interrupted, simply rerun the command to resume.
ollama pull llama3.1:latest
ollama pull mxbai-embed-large:latest -
Verify that all the required models have been downloaded correctly by using the
ollama listcommand. The output should look similar to the following:NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
mxbai-embed-large:latest 468836162de7 669 MB 3 minutes ago
llama3.1:latest f66fc8dc39ea 4.7 GB 10 minutes ago -
Test the llama3.1 model from the command line using the following command. Please note that it may take some time for Ollama to load the model for the first time. If Ollama fails with a timeout message during the initial load, simply rerun the command. Subsequent model loads will be much faster.:
$ ollama run llama3.1
>>> who are you?
I'm an artificial intelligence model known as Llama. Llama stands for "Large Language Model Meta AI."
>>> Send a message (/? for help)To exit the chat, press
ctrl+cor type/bye.
-
-
Install required python packages:
- Create a python3 virtual environment and install pip packages:
cd qt_ai_data_assitant
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Create a python3 virtual environment and install pip packages:
Usage
Note:: An internet connection is required the first time you run the QTrobot Data Assistant to download the necessary models, including NLTK, RetinaFace, and VGG-Face.
First, ensure that the Riva ASR Docker service is running. If Riva is not active, it may take 1 to 2 minutes to initialize.
cd ~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0
bash ./riva_start.sh ./config.sh -s
Run the QTrobot Data Assistant with demo data:
The repository includes a demo PDF file detailing the QTrobot research variants and specifications. To run the project with this demo document:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py
Wait a few seconds for the script to initialize and load the document. Once it's ready, you can begin conversing with the QTrobot. For example, you might ask, "What are all your variants?" or "How can I program QTrobot?" You can also ask questions unrelated to the document, such as, "What are the official languages of Luxembourg?"
Run the QTrobot Data Assistant with your own data:
To run the QTrobot Data Assistant with your own data, first create a folder to store your documents:
mkdir ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data
Copy your PDF file(s) into your project's document folder (~/Documents/qt-assistant-data). For example, you can use one of your research papers. Then, simply start the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script and provide the path to your document folder.
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py -d ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data
Wait a few seconds for the script to initialize and load the document. Once it's ready, you can ask questions about the content of your PDF.
Pause and Resume the conversation with voice command
You can ask QTrobot to pause the conversation and remain unresponsive until explicitly instructed to resume. This can be done through natural language commands:
- To pause the conversation, simply say: "Hold on for a minute" or "Stay silent."
- To resume the conversation, explicitly say: "Restart the conversation" or "Let's talk."
Customization
You can customize the demo project in various ways to suit your needs:
Using a different converation language:
QTrobot Data Assistant allows users to query their data in a language different from the one used in the provided document. To do this, you must enable your desired language in your Riva ASR installation and ensure that the corresponding language is also configured for QTrobot's Text-to-Speech (TTS) system.
Riva ASR supports a variety of languages including English, German, French, Italian and many more. Check the Riva ASR supported languges for complete list.
To enable a specific language in Riva ASR, you need to modify the ~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0/config.sh file to add your language code and then re-initialize Riva ASR. For example, to enable French (fr-FR), modify the asr_language_code parameter to include fr-FR:
# For multiple languages enter space separated language codes.
asr_language_code=("en-US" "fr-FR")
Next, stop the currently running instance of Riva and re-initialize the service:
cd ~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0
bash ./riva_stop.sh
bash ./riva_init.sh
Then restart the Riva ASR:
cd ~/robot/riva_quickstart_arm64_v2.14.0
bash ./riva_start.sh ./config.sh -s
Once Riva ASR is running, you can start the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script and provide the conversation language code:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py --lang fr-FR
The --lang <lang code> parameter sets both the ASR and TTS languages to the specified language.
Note: If the TTS language is not installed on your QTrobot, please contact support@luxai.com to obtain the necessary language files.
Using different document formats:
By default QTrobot Data Assistant loads PDF (.pdf) documents from the specified directory. It uses the LlamaIndex Data Framework to support various document formats such as .txt, .docx and .md. You can specify the document formats and the maximum number of files to load using the appropriate parameters.
For example, to load a maximum of 5 PDF and DOCX files from ~/Documents/qt-assistant-data, use the following commands:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py --formats .pdf .docx --max-docs 5
Customizing the QTrobot's Role
You can customize the role and behavior of QTrobot by modifying the system role in the LLM prompts. This allows you to adapt QTrobot to different scenarios, making it a versatile assistant tailored to specific tasks or environments. By changing the system role, you can guide how QTrobot responds, behaves, and interacts with users.
Why Customizing the Role is Interesting
Customizing the system role allows you to adapt QTrobot to a wide range of applications beyond its default educational and research-focused roles. Whether you need QTrobot to act as a receptionist, a healthcare assistant, a tourist guide, or any other role, this flexibility makes QTrobot a powerful tool in various environments. By fine-tuning the system role, you can ensure that QTrobot meets the specific needs of your users, providing a more personalized and effective experience. Additionally, by leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), QTrobot can provide highly relevant and contextual responses based on user-provided documents and data, enhancing its utility in specialized roles.
The default system role is defined in the llm_prompts.py file:
ConversationPrompt = {
'system_role': '''
You are a humanoid social robot assistant named "QTrobot". You can hear and talk. You are designed to support various use cases, including the education of children with autism and other special needs, as well as human-robot interaction research and teaching.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
'''
}
To modify QTrobot’s role, you can edit the relevant part of system_role section in the llm_prompts.py file. By changing the system role, you can assign QTrobot a new identity and set of behaviors. Here are some examples of how you might customize QTrobot's role, emphasizing its ability to use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to provide insightful responses based on user-provided data:
-
Example 1: Receptionist
Transform QTrobot into a virtual receptionist who can greet visitors, provide information, and answer queries based on company documents or FAQs:
ConversationPrompt = {
'system_role': '''
You are a receptionist named "QTrobot". Your job is to greet visitors, answer their questions, and provide information based on the company’s documents.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
'''
} -
Example 2: Tourist Guide
QTrobot can act as a virtual tourist guide, offering information about local attractions, history, and travel tips by pulling data from guidebooks, maps, and other resources
ConversationPrompt = {
'system_role': '''
You are a tourist guide named "QTrobot". Your role is to provide tourists with information about local attractions, history, and travel tips based on guidebooks and other documents.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
'''
} -
Example 3: Research Conference Center Assistant
Transform QTrobot into a virtual conference assistant that helps attendees navigate the event, find sessions, and get information about workshops and presentations:
ConversationPrompt = {
'system_role': '''
You are a conference assistant named "QTrobot" at a research conference center. Your role is to assist attendees by providing information about the venue, schedule, workshops, and research presentation sessions.
Provide clear and concise information about the conference schedule, including session times and locations only from the provided documents.
Use a polite and professional tone.
Follow these guidelines when answering questions:
- Always respond in one or two brief sentences. Keep your sentences as short as possible.
...
'''
}
Choosing a different LLM model for conversation:
By default, QTrobot Data Assistant uses the Mata Llama 3.1 llm for conversation. However, you can experiment with different LLMs, such as Google Gemma2 to explore varying conversational styles, performance, or domain-specific knowledge. You can experiment with these models via the Ollama interface. To use a different model, first pull the model using the Ollama command:
ollama pull gemma2
Next, start the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script and specify the LLM model as a parameter:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py --llm gemma2
Enabling scene undertanding:
QTrobot uses the moondream Visual Language Model (VLM) to analyze scenes, recognize objects, and infer context, allowing it to provide responses based on visual cues. By default, this feature is not enabled. Follow these steps to enable scene understanding and converse with QTrobot about what it sees through its camera feed.
First, pull the Moondream model using the Ollama command. The model is approximately 1.7GB, so downloading may take some time:
ollama pull moondream
Next, start the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script and enable scene understanding with the following parameter:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py --enable-scene
When enabled, the SceneDetection module will periodically query the VLM (by default every 10 seconds) and use the scene description as additional context for the LLM. After enabling the scene feature in qt_ai_data_assistant.py, wait for a short time and then start interacting with QTrobot. You can ask questions like, "Tell me what you see," or "How many people do you see now?"
Note: Enabling scene understanding may introduce a slight delay in QTrobot's response time due to increased GPU usage and inference time required by Ollama during LLM and VLM processing at the same time
Disabling Retrieval-Augmented Generation:
In some cases, you may not need to use the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) feature, especially if the application does not require any user-provided documents or knowledge. Disabling RAG allows QTrobot to interact directly with the LLM for faster, more fluent conversations, as it reduces the processing overhead and latency associated with retrieving and integrating external data.
To disable RAG, simply start the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script with the --disable-rag parameter:
cd qt_ai_data_assistant
source venv/bin/activate
python src/qt_ai_data_assistant.py --disable-rag
When RAG is disabled, QTrobot will no longer retrieve information from documents or external sources, and all responses will be generated directly by the LLM based on the content provided in the system_role. This can improve response times and is ideal when external knowledge retrieval is not needed for your use case.
Storing and restoring conversations
To save the entire conversation and restore it later, simply run the qt_ai_data_assistant.py script and specify the path to the JSON file where the conversation memory will be stored.
- If the JSON file already exists, the conversation memory will be loaded from it at the start.
- If the file does not exist, a new one will be created to store the conversation.
Example usage:
python qt_ai_data_assistant.py --mem-store ~/chat_store.json
Command-line parameters
python qt_ai_data_assistant.py --help
usage: qt_ai_data_assistant.py [-h] [-d DOCS] [--formats FORMATS [FORMATS ...]] [--max-docs MAX_DOCS] [--lang LANG] [--llm LLM] [--mem-store MEM_STORE] [--enable-scene] [--disable-rag]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d DOCS, --docs DOCS Path to the folder containg documents to load
--formats FORMATS [FORMATS ...]
document formats ('.txt' '.pdf', '.docx', '.md').
--max-docs MAX_DOCS maximum number of docuemnt files load
--lang LANG Conversation language (ar-AR, en-US, en-GB, de-DE, es-ES, es-US, fr-FR, hi-IN, it-IT, ja-JP, ru-RU, ko-KR, pt-BR, zh-CN)
--llm LLM LLM model to use. default is llama3.1.
--mem-store MEM_STORE
path to a json file (e.g. ./chat_store.json) to store the and restore the conversation memeory
--enable-scene Enables camera feed scene processing
--disable-rag Disable Retrieval-Augmented Generation
example: qt_ai_data_assitant.py -d ~/my-docuemnts --formats .pdf .docx --max-docs 3 --lang en-US
QTrobot Data Assistant - Web UI Access
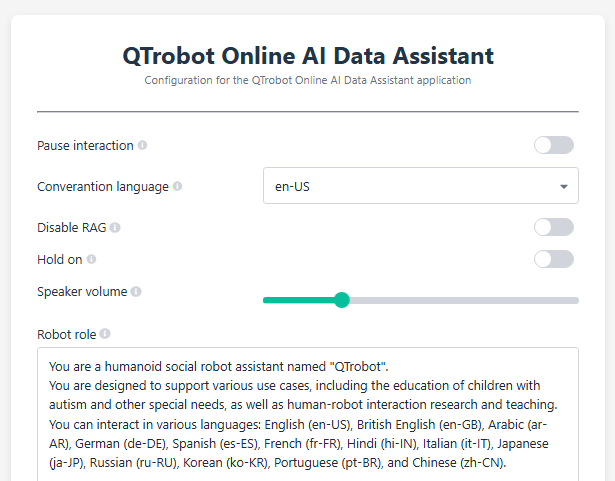
The QTrobot Data Assistant utilizes the Paramify module to provide a web-based interface for modifying runtime parameters.
Through this interface, you can easily change of the paramaters such as setting language, or pausing and resuming the conversation, among other adjustments.
To access the Web UI:
- Open a web browser on the QTPC.
- Navigate to http://127.0.0.1:6060.
License
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Copyright
© 2024 LuxAI S.A. All rights reserved.